Play with SDR and Intel Edison!
on
So some people already saw in my facebook that I started playing with SDRs (Software Defined Radio).
I always wanted to do my own radio receiver, and I did some in the past. But it’s very hard to adapt the radio for anything new you want do to, and also when you want to process data in your computer things become harder.
So a few months ago I found a nice tutorial of how to get NOAA Satellite Images using a cheap DVB-T (Digital Video Broadcast – Terrestrial) dongle that can be used as SDR. It costs about R$70 (roughly US$10) and the model I got (with R820T2 tuner) can tune from 24MHz to 1.74GHz!!!
What is inside this spectrum?
Actually a lot:
- FM Audio Radio Broadcasts
- VHF / UHF Television (Both Digital and Analog)
- Weather Satellites (APT, LRPT, HRPT)
- ADB-S (Air Traffic Telemetry)
- FM Air Traffic Radio
- And more
So my goal was to receive NOAA APT Signals (I even made a decoder!) but I don’t have a good enough antenna (yet).
The problem
So I made up a piece of antenna with two copper pipes (I call a piece, because its a dipole from a Double Cross Antenna) (I will make a tutorial later how to do it) to have better reception for the 2m band (~135Mhz) but every time a satellite was in range, I would need to go outdoor and turn on my laptop and start capturing. This was annoying.
The solution
So I though: I have an Intel Edison board here. Why not? Let’s make a remote Radio Receiver!
Pieces needed
- A Intel Edison
- A Box
- A RTL2832U Dongle ( Search for RTL SDR on Mercado Livre, Amazon, Ebay. You will find one)
- Power Supply for Edison
- (Optional) Custom Antenna to receive lower frequencies than UHF
So if you’re lazy to make a new antenna, just use the original one. It works very fine for strong signals. Sometimes I can even pickup a NOAA Satellite signal using it.
Compiling RTL-SDR in Edison
For our remote station we will need rtl_tcp program that opens a TCP Server to send the baseband packets through network to another machine. So for that we need to compile the rtl-sdr package from scratch.
One of its dependencies is the libusb, but there is no oficial Intel repository with it. So I used this tutorial: http://alextgalileo.altervista.org/edison-package-repo-configuration-instructions.html
So I will resume the tutorial. Just add the lines below to /etc/opkg/base-feeds.conf and run opkg update
src/gz all http://repo.opkg.net/edison/repo/all src/gz edison http://repo.opkg.net/edison/repo/edison src/gz core2-32 http://repo.opkg.net/edison/repo/core2-32
After that, lets install the libusb and git
opkg install libusb-0.1-dev git
Now we can compile the rtlsdr inside edison:
git clone git://git.osmocom.org/rtl-sdr.git mkdir build cd build cmake ../ make make install
So before continuing, the Edison Linux doesn’t have the ld.so.conf properly configured. So let’s do it! Fill the file with these lines:
/lib /usr/lib /usr/local/lib
And then run:
ldconfig
Now we can plug our dongle and see if everything is working fine! (Don’t forget to change the switch on the side of the USB conector to the direction towards the USB Plug!)
Plug it and run:
rtl_test
You should get a output like this:
root@TVS-RADIO:~# rtl_test Found 1 device(s): 0: Realtek, RTL2838UHIDIR, SN: 00000001 Using device 0: Generic RTL2832U OEM Found Rafael Micro R820T tuner Supported gain values (29): 0.0 0.9 1.4 2.7 3.7 7.7 8.7 12.5 14.4 15.7 16.6 19.7 20.7 22.9 25.4 28.0 29.7 32.8 33.8 36.4 37.2 38.6 40.2 42.1 43.4 43.9 44.5 48.0 49.6 [R82XX] PLL not locked! Sampling at 2048000 S/s. Info: This tool will continuously read from the device, and report if samples get lost. If you observe no further output, everything is fine. Reading samples in async mode...
Creating startup scripts
So now we just need to create the startup scripts to start rtl_tcp at boot. This is pretty simple, but as normal, the Linux of Edison is missing a few things. So let’s create /etc/init.d/ to put our startup script.
mkdir /etc/init.d
And then create a file called startsdr inside put:
#!/bin/bash ps | grep rtl\_tcp | grep -v grep if [ $? -eq 1 ] then nohup /usr/local/bin/rtl_tcp -a 0.0.0.0 & else echo "Already running" fi
and run:
chmod +x /etc/init.d/startsdr update-rc.d startsdr defaults
After that, the rtl_tcp should start automatically at boot.
The box
For the box, I just got a normal plastic box to put everything inside. Notice that I have a MCX -> BNC cable adapter, because I use a home-made external antenna. You can use your original one as well. So here are some pictures:



Testing it
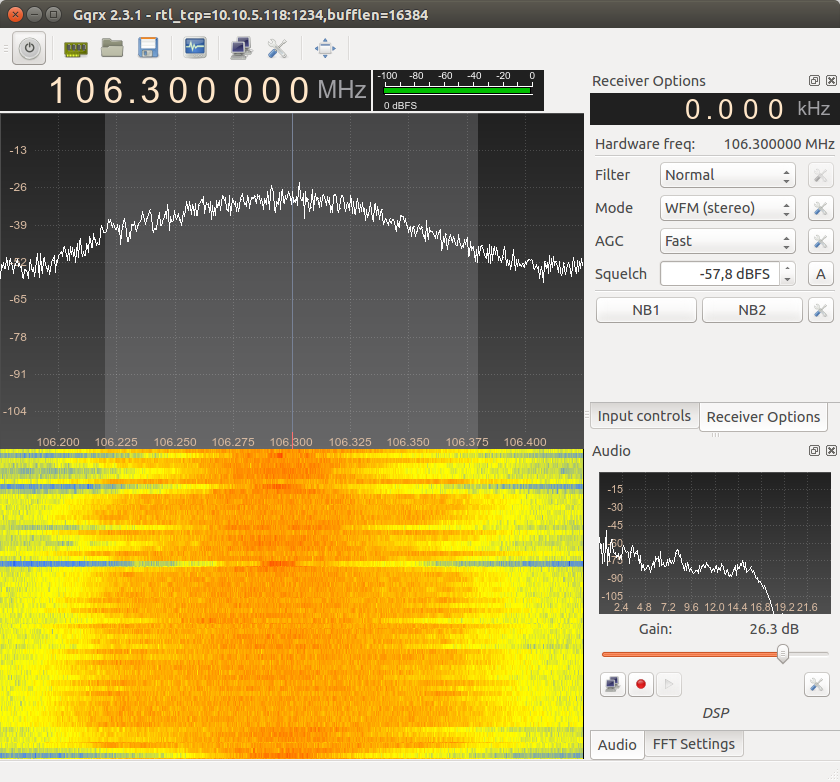
So now let’s test it! Have the IP Address of the Edison on the hand and go to your computer! Here I usually use Linux for testing stuff, so in linux you can use GQRX to connect to the SDR. For windows you can use SDR#
- Click on Configure I/O Devices

- Select RTL-SDR Spectrum Server at Device section.
- On Device string use rtl_tcp=YOUR_EDISON_IP:1234
- On Sample Rate you can select the sample rate (that implies in signal bandwidth). I usually uses 2.56MSps (2560000). But depending on the quality of the wifi signal on Edison, you may not be able to reach that sample rate (this is about 24Mbps of throuput on your wireless). For FM Radio receiving 250kSps (250000) should be enough.
- Keep Bandwidth in 0,000000 MHz
- Keep LNB LO in 0,000000 MHz
- Click OK
- Set the frequency in the Frequency Bar to a know FM Radio Frequency
- Set Filter to Normal in Receiver Options
- Set Mode to WFM (stereo)
- Click at Start DSP Processing

- Have fun!